Cabinet Design Software – using the clone functions to save time
SketchList 3D cabinet design software allows you to make exact copies of any object in your project by using the clone function. The clone function saves time by allowing you not to redesign the same part over and over again. (Somewhat related to this idea is the SketchList standard library where you can create an object design and save it for use in other places.) Imagine making a detailed cabinet with many shells, doors, and drawers and having to re-create that board by board each time. It’s much more efficient to simply select that assembly and clone it.
There are three types of clone within SketchList 3D.
- Clone – this makes an exact copy of the object highlighted.
- Clone and space – this makes any number of copies of the object. In addition it allows you to space the copies from bottom to top, left to right, or front to back.
- Clone and mirror – this allows you to make a copy of an object in mirror it 180° left or right.
There are different ways of initiating the clone command.
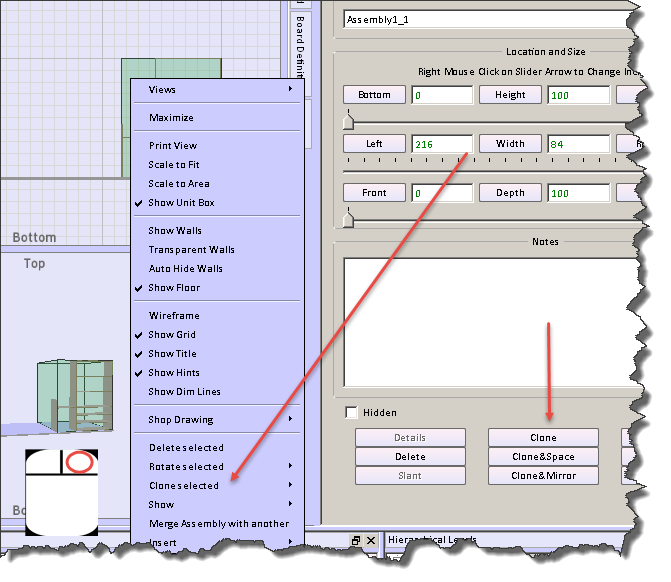
- There is a clone button on the object form to the right of the SketchList 3D main screen
- Right clicking the object opens a menu from which you can select the clone sub-menu. On that sub-menu you can pick any of the three clone techniques.
- Right clicking a row in the spreadsheet will open a menu from which you can select the type of clone you desire.
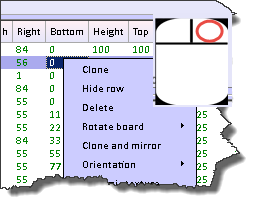
Cloning makes an exact copy of the original object. In the general spreadsheet you’ll notice the row is highlighted with the gold background. This means that an object has been cloned but not yet changed. This highlighting helps you see that there are indeed two objects in exactly the same space. When you change the name of the cloned object the gold highlighting will go away.
Usually the next step is to relocate the cloned object.
Clone and mirror makes a copy of the original object but inverts it left to right. If you had a bookshelf on the left of an assembly and drawers on the right cloning and mirroring would result in the second assembly where the drawers would be on the left and the bookshelf would be on the right.
Clone and space makes one or more copies of the original object. Objects may be clone and space in any of three directions – bottom to top, left to right, front to back.
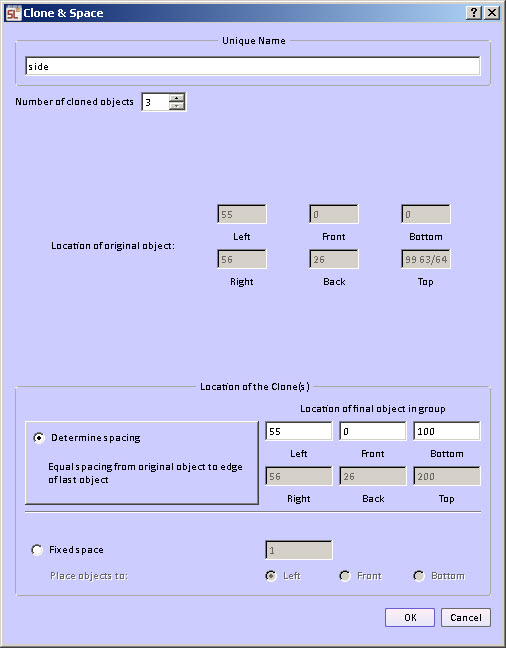
There are two different ways to do the spacing.
Fixed space between the cloned objects. The space between, for example, the tops of shelves and the bottom of the next shelf are equal for all pairs of shelves in the group. This way you can determine that the spacing between two objects would be a fixed amount, for example 10 units.
Variable space between cloned objects. The space between the objects is calculated over a span you specify. The beginning of the span is the original location of the selected object. You enter the end of the span. The ending of the span is set to the inside edge of the last object. For example if a bookcase height is 100 units and the thickness of the shelf is one unit the ending span would be set to 99. The form provides a calculation to show the top, right, back edge of the last copy of the object.
In fact with the variable spacing option you can clone and space the boards in more than one direction. In the example below the boards were cloned and then spaced in all three directions. This provides a bit of a staircase functionality in SketchList 3D.

Clone and space capability also exists within the round a non-round hole functions of SketchList 3D. In that case you can select a hole and clone and space it.